Running a PHP script forever with Supervisor
Let’s say you want to run a script forever (like a job queuing system that needs to constantly listen to incoming jobs) you could just start the process with a php my-script.php and be done with it (HAHA jk) but then how do you make sure it always run? And what if you want to monitor it?
I saw in the past people relying on crontabs (@reboot) and doing a screen of their scripts. the problem with this approach is that your script might die for whatever reason and won’t restart.
I stumbled upon a nice process control system called Supervisor which will make sure your scripts run and will even give you a nice web interface :)
Install Supervisor
sudo apt-get install supervisorThe above command will install the supervisor service in your /etc/ that you can start, stop, restart, force-reload, status, force-stop.
If you look at the /etc/supervisor/supervisord.conf config file, you’ll see that supervisor includes config files in /etc/supervisor/conf.d/*.conf. Let’s create one for our forever running php script.
sudo vi /etc/supervisor/conf.d/are-we-there-yet.conf
# and paste the below
[program:are_we_there_yet]
command=php /var/www/areWeThereYet.php
numprocs=1
directory=/tmp
autostart=true
autorestart=true
startsecs=5
startretries=10
redirect_stderr=false
stdout_logfile=/var/www/are-we-there-yet.out.log
stdout_capture_maxbytes=1MB
stderr_logfile=/var/www/are-we-there-yet.error.log
stderr_capture_maxbytes=1MBAnd now let’s create our dummy php script file:
<?php
while (true) {
echo 'Are we there yet??'.PHP_EOL;
sleep(5);
}
?>I know - awesome script right?
So let’s save all that and restart our supervisor:
sudo service supervisor restart
# check if supervisor is running
ps -auxf | grep supervisor
# check if your php script is running
ps -auxf | grep phpYou should see the python process running (/usr/bin/python /usr/bin/supervisord -c /etc/supervisor/supervisord.conf) and your awesome (haha) script (\_ php /var/www/areWeThereYet.php) also running in the background, populating your two logs defined in the supervisor config.
Web interface of logs
sudo vi /etc/supervisor/supervisord.conf
# Add this bit at the end:
[inet_http_server]
port=9001
username = YourUsernameHere
password = YourPasswordHereRestart supervisor and now if you have a http server (restart it as well) you can go on http://localhost:9001 fill in username/password and access the supervisord web interface.
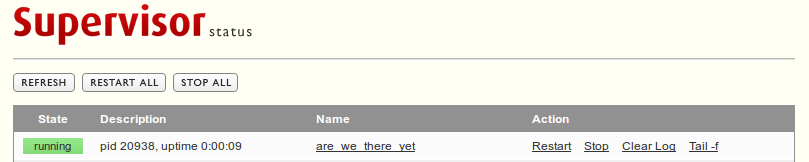 Supervisor web interface
Supervisor web interface